Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a gastrointestinal disorder that can last for months, years, or even a lifetime. Affecting approximately 10% of the population, IBS can range from mildly uncomfortable to severely painful, making daily life a challenge for those affected. To better understand this often-overlooked condition, let’s answer some important questions:
- What are the causes and symptoms of IBS?
- How can you manage, relieve, and prevent it?

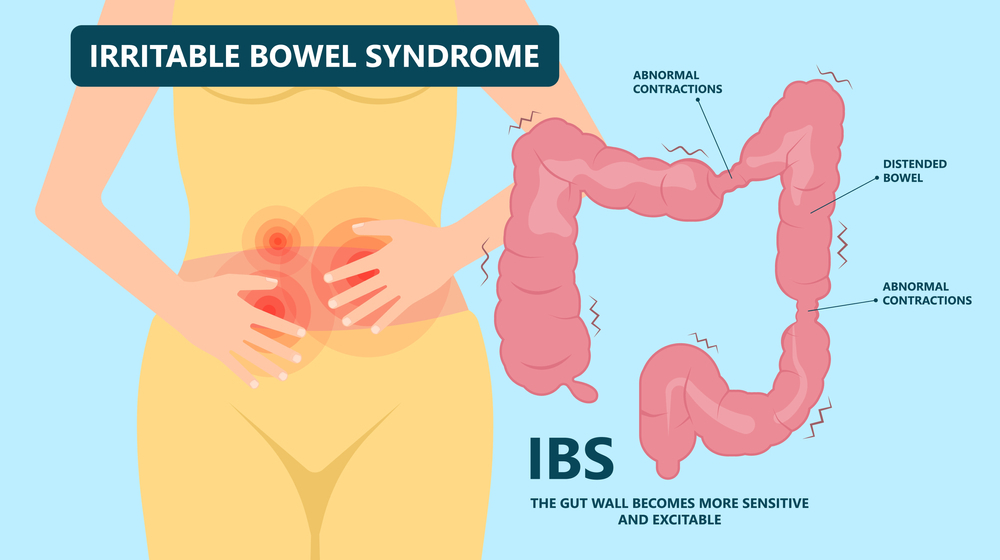
What is IBS?
IBS is categorized into four subtypes based on the symptoms a person experiences:
- IBS-U (Unsubtyped): Symptoms that don’t fit into the other categories or occur less than 25% of the time.
- IBS-D (Diarrhea-predominant): Loose or watery stools more than 25% of the time.
- IBS-C (Constipation-predominant): Hard or lumpy stools that make bowel movements difficult more than 25% of the time.
- IBS-M/IBS-A (Mixed/Alternating): A combination of IBS-D and IBS-C, each occurring at least 25% of the time.
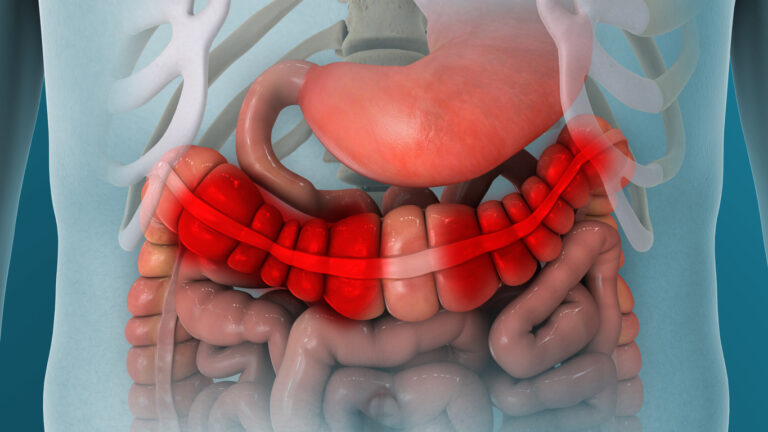
What causes IBS?
IBS is thought to result from dysfunction in the gut, particularly involving the muscles and nerves responsible for bowel sensation and motility. Several factors contribute to this dysfunction, including:
- Vitamin D
- Deficiency
- Gut Microbiota Imbalances: Fungus or bacteria affecting the digestive system.
- Post-Infection Complications: Such as gastroenteritis.
- Stress and
- Anxiety
- Genetics
Symptoms of IBS
Symptoms of IBS vary but commonly include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping.
- Diarrhea or constipation (or alternating between the two).
- Bloating and excessive gas.
- Urgency to use the bathroom.
- Fatigue and disrupted sleep.
Managing, Relieving, and Preventing IBS
While there is no universal cure for IBS, several strategies can significantly improve symptoms and help manage the condition:
Dietary Changes
- Low FODMAP Diet: Avoid carbohydrates that are poorly absorbed in the small intestine, such as fructose, sorbitol, and xylitol.
- Fiber Intake: Soluble fiber supplements, like psyllium husk, can help regulate bowel movements.
Medications and Supplements
- Laxatives: Useful for IBS-C, IBS-M, and IBS-U to ease constipation.
- Antidepressants: Can help treat IBS symptoms, even in individuals not using them for depression.
- Probiotics: Encourage healthy gut microbiota, potentially reducing IBS symptoms.
- Nutritional Supplements: Combine strategies like enzyme support, anti-inflammatory ingredients, and gut-healing compounds.
Natural and Herbal Remedies
- Peppermint Oil: Soothes the digestive tract, reduces bloating, and alleviates pain.
- Ginger: Eases inflammation and improves digestion.
- Aloe Vera: Acts as a natural laxative and detoxifier.
- Turmeric: Reduces stomach pain and regulates bowel movements.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Stress Management: Practices like yoga and meditation can alleviate IBS symptoms.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Addresses stress and its impact on IBS.
- Regular Exercise: At least 30 minutes daily can reduce anxiety and improve digestive health.
Essential Ingredients in IBS Supplements
Research highlights key ingredients that help combat IBS symptoms:
- Vitamin D: Deficiency is common among IBS sufferers and should be supplemented.
- Digestive Enzymes: Include protease, amylase, and lipase to aid in breaking down food and improving gut health.
- Psyllium Husk: Soluble fiber that cleanses the intestines.
- Peppermint/Perilla: Reduces bloating, cramping, and pain while improving overall gastrointestinal health.
- Aloe Vera & Turmeric: Anti-inflammatory and detoxifying properties to support a healthy digestive system.

All You Need to Know About IBS: Causes, Symptoms, and Relief
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a gastrointestinal disorder that can last for months, years, or even a lifetime. Affecting approximately 10% of the population, IBS can range from mildly uncomfortable to severely painful, making daily life a challenge for those affected. To better understand this often-overlooked condition, let’s answer some important questions:
- What are the causes and symptoms of IBS?
- How can you manage, relieve, and prevent it?
What Is IBS?
IBS is categorized into four subtypes based on the symptoms a person experiences:
- IBS-D (Diarrhea-predominant): Loose or watery stools more than 25% of the time.
- IBS-C (Constipation-predominant): Hard or lumpy stools that make bowel movements difficult more than 25% of the time.
- IBS-M/IBS-A (Mixed/Alternating): A combination of IBS-D and IBS-C, each occurring at least 25% of the time.
- IBS-U (Unsubtyped): Symptoms that don’t fit into the other categories or occur less than 25% of the time.
What Causes IBS?
IBS is thought to result from dysfunction in the gut, particularly involving the muscles and nerves responsible for bowel sensation and motility. Several factors contribute to this dysfunction, including:
- Vitamin D Deficiency
- Gut Microbiota Imbalances: Fungus or bacteria affecting the digestive system.
- Post-Infection Complications: Such as gastroenteritis.
- Stress and Anxiety
- Genetics
Symptoms of IBS
Symptoms of IBS vary but commonly include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping.
- Diarrhea or constipation (or alternating between the two).
- Bloating and excessive gas.
- Urgency to use the bathroom.
- Fatigue and disrupted sleep.
Managing, Relieving, and Preventing IBS
While there is no universal cure for IBS, several strategies can significantly improve symptoms and help manage the condition:
Dietary Changes
- Low FODMAP Diet: Avoid carbohydrates that are poorly absorbed in the small intestine, such as fructose, sorbitol, and xylitol.
- Fiber Intake: Soluble fiber supplements, like psyllium husk, can help regulate bowel movements.
Medications and Supplements
- Laxatives: Useful for IBS-C, IBS-M, and IBS-U to ease constipation.
- Antidepressants: Can help treat IBS symptoms, even in individuals not using them for depression.
- Probiotics: Encourage healthy gut microbiota, potentially reducing IBS symptoms.
- Nutritional Supplements: Combine strategies like enzyme support, anti-inflammatory ingredients, and gut-healing compounds.
Natural and Herbal Remedies
- Peppermint Oil: Soothes the digestive tract, reduces bloating, and alleviates pain.
- Ginger: Eases inflammation and improves digestion.
- Aloe Vera: Acts as a natural laxative and detoxifier.
- Turmeric: Reduces stomach pain and regulates bowel movements.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Addresses stress and its impact on IBS.
- Regular Exercise: At least 30 minutes daily can reduce anxiety and improve digestive health.
- Stress Management: Practices like yoga and meditation can alleviate IBS symptoms.
Essential Ingredients in IBS Supplements
Research highlights key ingredients that help combat IBS symptoms:
- Vitamin D: Deficiency is common among IBS sufferers and should be supplemented.
- Digestive Enzymes: Include protease, amylase, and lipase to aid in breaking down food and improving gut health.
- Psyllium Husk: Soluble fiber that cleanses the intestines.
- Peppermint/Perilla: Reduces bloating, cramping, and pain while improving overall gastrointestinal health.
- Aloe Vera & Turmeric: Anti-inflammatory and detoxifying properties to support a healthy digestive system.
The Path to Better Gut Health
IBS is a complex condition with no one-size-fits-all solution. However, understanding your symptoms, identifying triggers, and adopting a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and targeted supplements can provide significant relief.
If you’re struggling with IBS, consult with a healthcare provider to create a tailored management plan that addresses your unique needs. With the right approach, you can take control of your symptoms and improve your quality of life.






What about hypnotherapy?
Meditation is a form of neural relaxation that helps reduce stress and fatigue. However, it does not have a significant effect on IBS.